Top 5 Relief Valve Options for Optimal Pressure Control in Industrial Applications
In the dynamic world of industrial applications, effective pressure control is paramount to ensure safety and operational efficiency. As experts like Dr. Emily Carter, a renowned specialist in pressure management systems, emphasize, “The right relief valve is not just a component; it’s a critical safeguard that can prevent catastrophic failures.” With the increasing complexity of industrial systems, selecting the appropriate relief valve is essential not only for compliance with safety regulations but also for optimizing performance and minimizing downtime.
This article explores the top five relief valve options that promise to enhance pressure control across various industrial sectors. Each of these solutions offers unique advantages tailored to specific operational needs, ensuring that pressure remains within optimal levels while safeguarding equipment and personnel. By understanding the features and applications of these relief valves, engineers and facility managers can make informed decisions that contribute to the longevity and reliability of their systems. Ultimately, the right choice in relief valve technology stands as a pillar of industrial safety and efficiency.
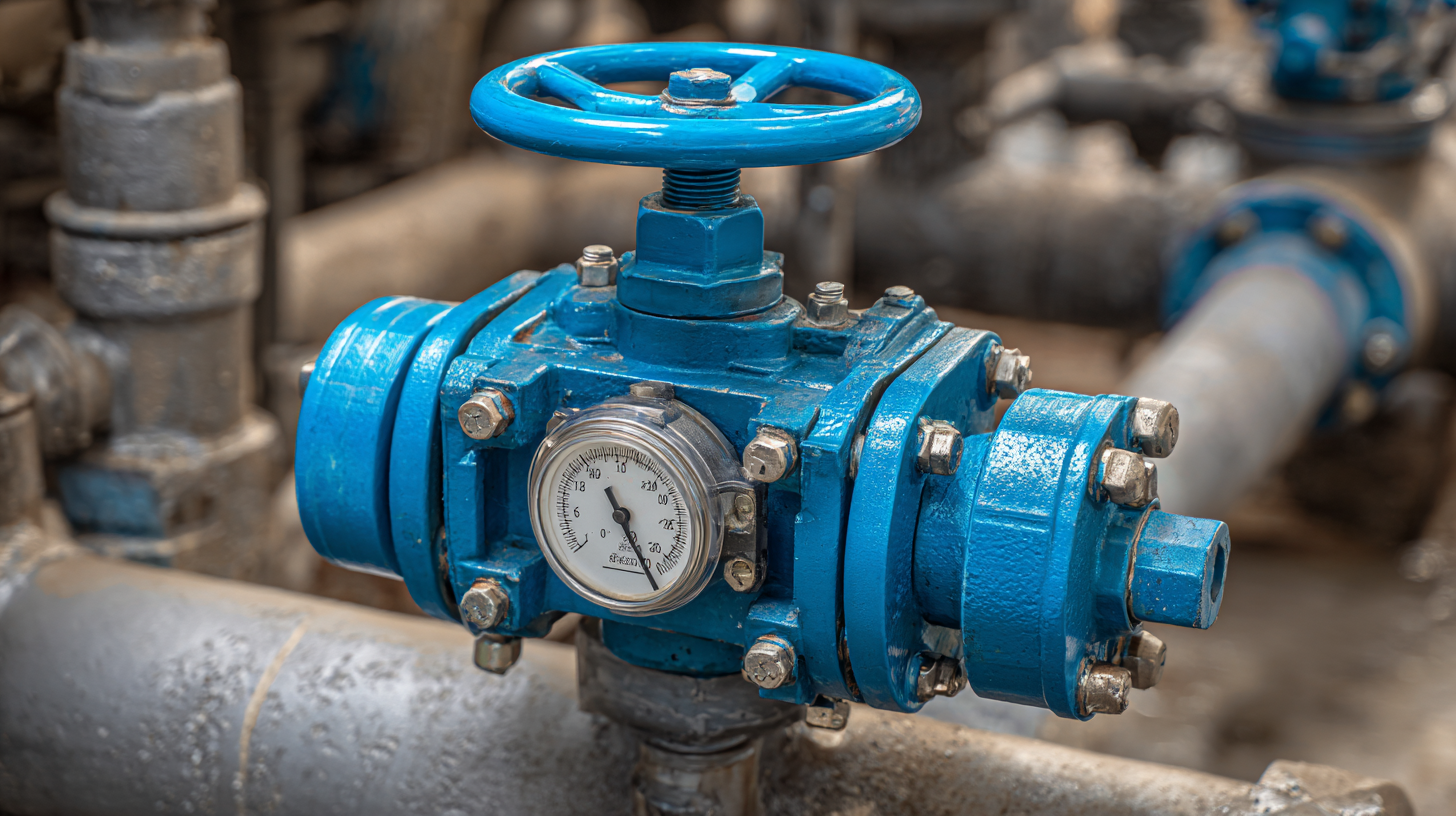

Key Considerations for Selecting Relief Valves in High-Pressure Systems
When selecting relief valves for high-pressure systems, several
key considerations must be addressed to ensure optimal pressure control and system safety.
First and foremost, understanding the set pressure is crucial.
This value should be carefully determined based on the system's maximum allowable working pressure
(MAWP) and must comply with industry standards such as those from the
American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), which recommends that relief valves
should be set at or below the MAWP to prevent potential equipment failure
(ASME BPVC Section VIII).
Material compatibility is another critical factor, particularly in corrosive environments.
According to a report by the National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors,
over 30% of valve failures occur due to improper material selection, leading to corrosion and
erosion-related issues. High-performance materials, such as stainless steel or
alloy compositions, are often recommended for demanding applications to increase longevity and
reliability. Additionally, the sizing of the relief valve is essential; it must be adequate to
handle the calculated flow rate in emergency situations. A study presented in the
Pressure Relief Device Symposium highlights that improper sizing can result in
insufficient discharge capacity, posing significant risks to equipment and personnel.
Furthermore, the choice between pilot-operated and spring-operated
relief valves can influence operational efficiency. Pilot-operated valves tend to provide better
control over fluctuations in pressure and are favorable in systems where tight regulation is needed.
Conversely, spring-operated valves are simpler and often less expensive, making them a viable option
for less critical applications. By carefully considering these aspects, engineers can select the
right relief valve that not only meets safety regulations but also enhances the overall efficiency
of high-pressure systems.
Impact of Material Choices on Relief Valve Longevity and Reliability
In the realm of industrial applications, the longevity and reliability of relief valves are profoundly influenced by the materials chosen for their construction. According to a report from the International Journal of Pressure Relief System Engineering, using high-alloy metals can significantly enhance resistance to corrosion and wear, which are critical factors in prolonging the life of relief valves. For instance, stainless steel and Inconel are often favored due to their exceptional mechanical properties and resilience to harsh environments, reducing the frequency of replacements and maintenance costs.

Tip: Always assess the operating environment and fluid characteristics before selecting materials for relief valves. The compatibility of materials with the substances they will encounter can prevent failures and extend operational efficiency.
Moreover, it’s essential to consider the impact of temperature fluctuations and pressure variability on material integrity. Research indicates that materials like carbon steel may perform adequately under standard conditions but may struggle under extreme temperatures, which can lead to premature fatigue. This emphasizes the need for comprehensive evaluations including stress tests and lifespan predictions during the material selection process.
Tip: Regularly evaluate the operational conditions and inspect relief valves for signs of material degradation. Proactive maintenance is key to ensuring long-term reliability and performance.
Performance Metrics: Flow Capacity and Response Time of Relief Valves
When selecting a relief valve for industrial applications, performance metrics such as flow capacity and response time are critical components to consider. Flow capacity measures how much fluid a valve can handle before it reaches a set pressure, directly influencing the effectiveness of pressure control. A higher flow capacity ensures that the valve can manage sudden surges in pressure without failing, which is vital in maintaining system integrity and safety.
Response time, on the other hand, refers to how quickly the valve reacts to changes in pressure. A quick response time is essential for preventing pressure build-up that could lead to equipment damage or hazardous conditions. For optimal performance, choose a valve design that demonstrates both a high flow capacity and rapid response time.
**Tip 1:** Always check the specifications of the relief valve to ensure it meets the demands of your specific application.
**Tip 2:** Regular maintenance and testing of relief valves can significantly improve their reliability and performance in high-pressure situations.
**Tip 3:** Consider valves made from durable materials that can withstand harsh environments to prolong their lifespan and ensure consistent operation.
Top 5 Relief Valve Options for Optimal Pressure Control in Industrial Applications
| Relief Valve Type | Flow Capacity (Cv) | Response Time (ms) | Max Pressure (psi) | Temperature Range (°F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring-Loaded | 0.5 - 10 | 50 | 200 | -40 to 350 |
| Pilot-Operated | 10 - 120 | 150 | 300 | -20 to 250 |
| Deadweight | 2 - 50 | 30 | 600 | 0 to 300 |
| Safety Valve | 1 - 20 | 100 | 350 | -40 to 400 |
| Burst Disc | 5 - 100 | 10 | 1000 | -20 to 500 |
Regulatory Compliance and Standards Affecting Relief Valve Selection
When selecting relief valves for industrial applications, understanding regulatory compliance and standards is crucial. Various organizations, such as the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), set guidelines that ensure safety and performance. Compliance with these standards not only helps in meeting legal requirements but also mitigates risks associated with overpressure scenarios. Industries must carefully consider these regulations when choosing relief valves to avoid costly fines and ensure operational integrity.

Furthermore, different sectors may have unique regulations that influence relief valve selection. For instance, the oil and gas industry often adheres to more stringent safety standards due to the potentially hazardous nature of the materials involved. Similarly, the chemical manufacturing sector must comply with the Process Safety Management (PSM) regulations, which necessitate the use of valves that can withstand extreme conditions and prevent catastrophic failures. By aligning valve selection with these standards, companies can enhance safety, ensure reliability, and maintain compliance in their operations.
Innovative Technologies Enhancing Relief Valve Efficiency in Industrial Settings
In industrial applications, the efficiency of relief valves is paramount for ensuring optimal pressure control and safety. Innovative technologies have emerged that enhance the performance of these critical components, focusing on precision, responsiveness, and durability. For instance, advanced materials and manufacturing techniques have led to the creation of lightweight yet robust relief valves that can withstand extreme conditions while minimizing wear and tear. Additionally, the integration of smart sensors enables real-time monitoring of pressure levels, allowing for immediate adjustments and reducing the risk of system failures.
Another noteworthy advancement is the incorporation of digital controls in relief valve systems. These controls facilitate automatic regulation based on fluctuating pressure conditions and operational demands, minimizing the need for manual intervention. Furthermore, machine learning algorithms analyze historical data to predict potential pressure surges, enabling preemptive actions that enhance system reliability. With these innovative technologies, industries can achieve better pressure management, ensure compliance with safety standards, and significantly lower operational costs.
Top 5 Relief Valve Options for Optimal Pressure Control in Industrial Applications
Related Posts
-
Exploring ASCO Solenoids: The Backbone of Modern Automation in Industries
-

Understanding Pressure Relief Valves: Key Specifications and Their Crucial Role in Industrial Safety
-

Exploring the Future of Valve Automation and Control in Sustainable Energy Solutions
-

Understanding the Importance of Gas Valves in Home Safety and Efficiency
-

Understanding the Importance of Flow Control Valves in Modern Industrial Applications
-
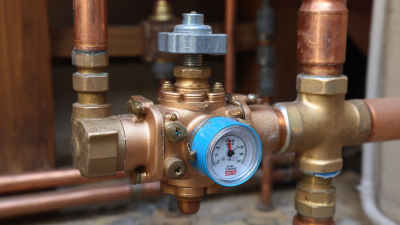
Exploring the Benefits of Installing a Water Pressure Relief Valve in Your Home Plumbing System

